Building an ERM Program: Top 10 Risk Management Fundamentals, Part 1
- December 5, 2019
- Quantivate
The Risk Management Society (RIMS) defines enterprise risk management, or ERM, as “a strategic business discipline that supports the achievement of an organization’s objectives by addressing the full spectrum of its risks and managing the combined impact of those risks as an interrelated risk portfolio.”
If a strategic, comprehensive, integrated approach to assessing and managing risk is the ultimate goal — then what specific elements make up a successful ERM program? Let’s take a tour of 10 program categories that encompass the risk management fundamentals your organization needs to build a complete and effective ERM program.
We’ll cover the first five fundamentals in this article, and the remaining five in next week’s installment.
Risk Management Fundamentals
*click to jump to section
-
- Risk Management Policies & Procedures
- Risk Management Leader
- Committee(s) and Charter(s)
- Risk Management Framework
- Risk Assessments
- Risk Appetite Statement With Thresholds
- Key Indicators
- Reporting
- Risk Management Training
- Ongoing ERM Program Growth & Maturity
Risk Management Policies & Procedures
Policy types:
- ERM
- Compliance
- Vendor Management
- Information Security
- Business Continuity
- Audit
Items to include in each policy:
- Management and/or senior executive approval date
- Board approval date
- Applicable laws and regulations
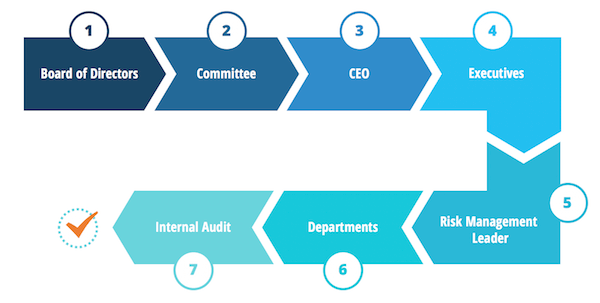
- Areas of responsibility — board of directors, committee(s), CEO, executive management, head of risk, departments/staff, internal audit
- Summary of risk management approach
- Purpose of policy
- Risk management overview
- Risk management mission
- Risk management definitions — to ensure consistency when discussing risk
- Risk appetite / tolerance — defines an acceptable level of risk in the pursuit of overall financial, value, and performance goals
- Risk categories — the areas where you want to determine risk according to your organization’s objectives, initiatives, products/services, and processes
- Approach to risk management
- Information and communication
- Monitoring activities and correcting deficiencies
- Policy management / documentation & review
- Procedures to support the execution of policies
Learn more → Take stock of other risk management foundations
with this quick ERM Program Checkup.
Risk Management Leader
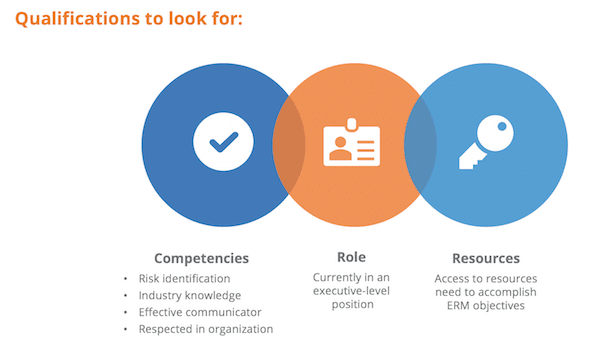
Required competencies & characteristics:
- Risk identification
- Industry knowledge
- Respected throughout the organization
- Highly effective communicator
ERM Committee(s) and Charter(s)
ERM Committee
Include key employees representing executive management and potentially department management to ensure cross-functional risk discussions.
Responsibilities:
- Establish risk measurement
- Set ERM objectives
- Determine appropriate reporting processes
- Promote a risk-based culture
ERM Charter
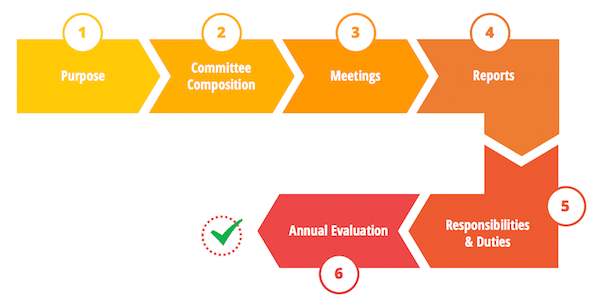
At minimum, include the following:
- Purpose
- Committee composition
- Meetings
- Reports
- Scope of committee’s responsibilities
- Annual evaluation
Learn more → What’s Your Risk Culture?
Risk Management Framework
Define your:
- Strategic and operational approaches to risk management
- Risk categories and definitions
- Qualitative and quantitative metrics, including:
- Risk likelihood: the probability that a given risk event will occur
- Risk impact: the extent to which a given risk event might impact the organization’s assets and/or capital
- Control ratings: assessment of a control’s strength
- Control effectiveness: assessment of a control’s ability to achieve the expected or intended outcome
- Risk velocity: the time it takes a risk event to manifest itself
- Risk vulnerability: an organization’s susceptibility to a risk event as determined by its preparedness, agility, and adaptability
- Overall risk rating
Learn more → Brush up on these and other ERM terms with this Risk Management Glossary.
Risk Assessments

Assess your:
- Strategic plans
- Business operations (departmental business processes)
- Products / services
Risk assessment steps:
- Determine your inherent risk across significant risk areas using likelihood and impact ratings
- Prioritize risk assessment based on inherent risk scores
- Discuss and rate the controls currently in place, beginning with the areas with the most inherent risk
- Apply the appropriate vulnerability to the overall process being assessed
- Apply the appropriate velocity to the specific risks identified
Learn more → Risk Management: Top 7 Risk Assessment Tips
Don’t miss exploring 5 more risk management fundamentals
Come back next week to learn about techniques for measuring and monitoring risk, including risk appetite, key indicators, and more. Subscribe to the Quantivate blog using the form at the top of this page to be one of the first to get the latest content and updates.
Read “Building an ERM Program: Top 10 Risk Management Fundamentals, Part 2”